Understanding The Hub In: A Comprehensive Guide
The term "hub in" has gained significant traction in various fields, particularly in technology and logistics. This concept is integral to understanding how connectivity and efficiency are achieved in modern systems. In this article, we will explore the multifaceted nature of hub in, its applications, and its implications for businesses and consumers alike. By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of what hub in means and how it can impact various sectors.
As organizations continue to seek ways to optimize their operations, the hub in concept emerges as a vital strategy. Whether in transportation, data management, or supply chain logistics, understanding hub in can lead to enhanced performance and productivity. We'll delve into the core principles of this concept and highlight its relevance in today's fast-paced world.
This article is structured to provide you with detailed insights into hub in, including its definition, benefits, applications, and future trends. With the rise of digital transformation, it is crucial to grasp how hub in operates within different contexts and its potential to revolutionize traditional systems.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is Hub In?
- 2. Benefits of Hub In
- 3. Applications of Hub In
- 4. Hub In in Logistics
- 5. Hub In in Technology
- 6. Hub In in Data Management
- 7. Future Trends of Hub In
- 8. Conclusion
1. What is Hub In?
Hub in refers to a central point or node in a network or system where various components converge to facilitate communication, data transfer, or logistics. This concept can be applied across different sectors, including transportation, technology, and data management.
In essence, a hub serves as an intermediary that connects various parts of a system, enabling efficient interaction and flow of information or resources. It plays a crucial role in streamlining operations and enhancing overall functionality.
2. Benefits of Hub In
The implementation of hub in strategies yields numerous benefits for organizations and consumers. Some of the key advantages include:
- Exploring The Life And Journey Of Tim Duncans Wife A Deep Dive
- David Labravas Wife A Deep Dive Into Their Relationship
- Increased Efficiency: By centralizing processes, organizations can significantly reduce time and resource wastage.
- Improved Communication: Hubs foster better communication between different parts of a system, leading to more effective collaboration.
- Cost Savings: Streamlined operations often result in lower operational costs.
- Scalability: Hubs can easily adapt to increased workloads, making them ideal for growing businesses.
3. Applications of Hub In
Hub in can be applied in various contexts, each with its unique characteristics and requirements. Some notable applications include:
3.1 Transportation and Logistics
In the transportation sector, hub in plays a vital role in managing freight and passenger movement. Hubs serve as central points where goods and services are consolidated before distribution to various destinations.
3.2 Technology and Networking
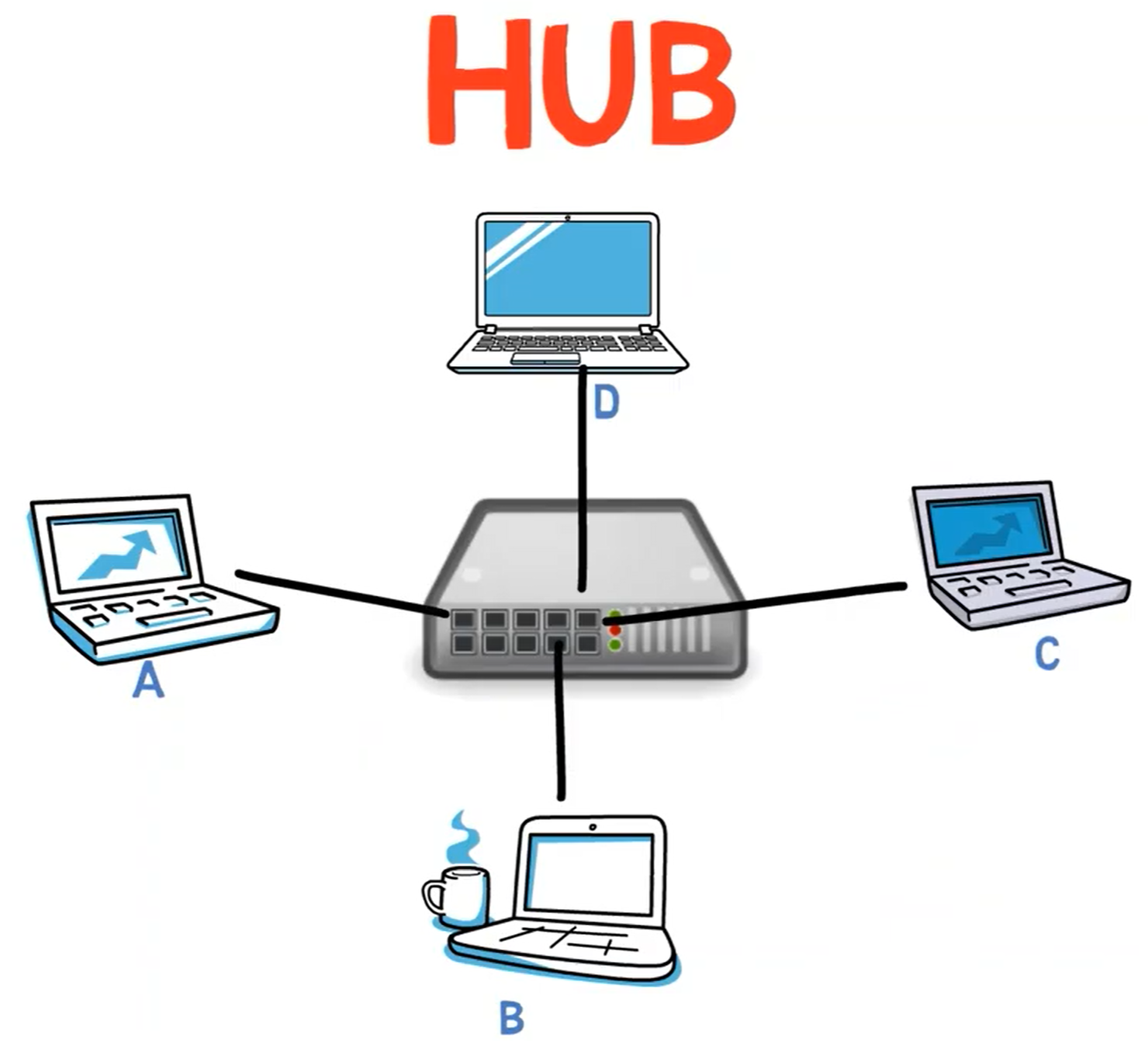
In technology, hub in refers to network hubs that facilitate data transfer between devices. These hubs are essential for maintaining connectivity and ensuring efficient communication in networks.
4. Hub In in Logistics
The logistics industry heavily relies on hub in strategies to optimize supply chain operations. By utilizing central hubs, logistics companies can:
- Consolidate Shipments: Reduce the number of trips required for deliveries.
- Enhance Tracking: Improve visibility of shipments throughout the supply chain.
- Minimize Delays: Streamline operations to ensure timely deliveries.
5. Hub In in Technology
In the realm of technology, hub in is often associated with network architecture. Network hubs are devices that allow multiple Ethernet devices to connect and communicate within a network. Key features include:
- Data Packet Distribution: Network hubs facilitate the transmission of data packets between devices.
- Signal Amplification: They help strengthen signals to ensure data integrity over longer distances.
6. Hub In in Data Management
Data management is another area where hub in concepts are crucial. Centralized data hubs allow organizations to:
- Integrate Data Sources: Consolidate data from various sources for comprehensive analysis.
- Enhance Data Quality: Improve the accuracy and reliability of data through centralized management.
7. Future Trends of Hub In
As technology continues to evolve, the hub in concept is expected to undergo significant changes. Some future trends to watch include:
- Increased Automation: Automation technologies will further streamline operations and reduce manual intervention.
- Integration with AI: Artificial intelligence will enhance decision-making processes within hubs.
8. Conclusion
In summary, hub in is a powerful concept that enhances efficiency, communication, and cost-effectiveness across various sectors. Understanding its applications and benefits can provide organizations with a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced environment. We encourage you to explore how hub in can be applied to your own operations and consider the potential advantages it may bring.
Feel free to share this article, leave a comment, or check out other resources on our site for more insights into modern strategies and technologies.
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you back here for more informative articles.
- Puffiddy And Jay Z The Dynamic Duo Of Hiphop
- Brittany Force Boyfriend The Love Life Of A Racing Champion
Network Devices How Hubs and Switches Work and How to Secure Them

Powered USB Hub, RSHTECH 7Port Powered USB 3.0/USB C Hub with 14 Mode

What is Hub in Computer Networks? Shiksha Online