Understanding Proxy: A Comprehensive Guide To Online Privacy And Security
In today's digital age, the term "proxy" has become increasingly relevant as individuals seek ways to protect their online privacy and enhance security. A proxy server acts as an intermediary between a user and the internet, allowing for anonymous browsing, data encryption, and access to restricted content. Understanding the nuances of proxy technology is essential for anyone looking to safeguard their personal information and enhance their online experience.
This article will delve into the intricacies of proxy servers, exploring their types, benefits, and potential drawbacks. We will also discuss how proxies can be effectively utilized to maintain privacy online while navigating the complexities of the internet. With the rise of cyber threats and the increasing importance of data protection, having a solid grasp of proxy technology is more crucial than ever.
Whether you are a casual internet user, a business professional, or someone seeking to enhance your online privacy, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the world of proxies. Let's embark on this journey to understand what a proxy is, how it functions, and why it may be the solution you need for your online security.
- Morgan Freeman The Iconic Voice And Legendary Actor
- Michael Landons Last Performance A Tribute To A Legendary Actor
Table of Contents
- What is a Proxy?
- Types of Proxies
- Benefits of Using Proxies
- Drawbacks of Proxies
- How to Choose a Proxy
- Proxy vs. VPN: What’s the Difference?
- Proxy Usage in Business
- The Future of Proxies
What is a Proxy?
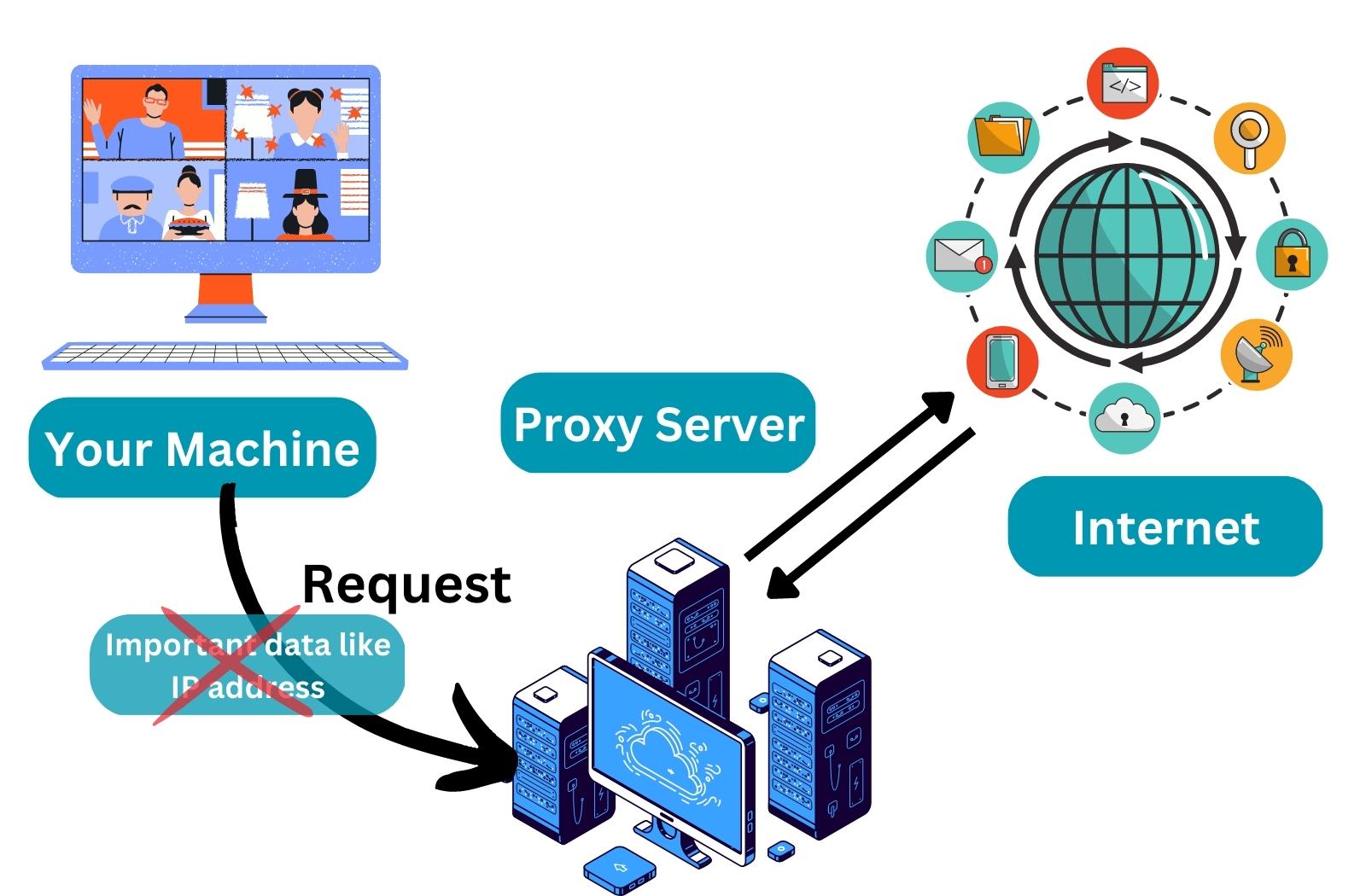
A proxy server is a computer system or router that acts as a gateway between users and the internet, enabling users to make indirect network connections to other network services. When a user connects to the internet through a proxy, their requests for web pages and resources are sent to the proxy server first. The proxy then forwards these requests to the appropriate web server, retrieves the response, and sends it back to the user.
Proxies serve several purposes, including:
- Improving online privacy by hiding users' IP addresses.
- Bypassing geo-restrictions and accessing blocked content.
- Enhancing security by filtering out malicious content.
Types of Proxies
There are various types of proxy servers, each designed to cater to specific needs and use cases. Understanding these types can help users select the most appropriate one for their requirements.
1. HTTP Proxies
HTTP proxies are specifically designed for web traffic. They work with the HTTP protocol and can cache web pages for faster access. However, they do not encrypt traffic, making them less secure for sensitive data transactions.
2. HTTPS Proxies
HTTPS proxies, unlike HTTP proxies, encrypt the data exchanged between the user and the web server. This makes them a better choice for secure transactions and sensitive information sharing.
3. SOCKS Proxies
SOCKS proxies operate at a lower level and can handle any kind of traffic, including HTTP, FTP, and P2P. They are versatile but may require additional configuration compared to HTTP proxies.
4. Transparent Proxies
Transparent proxies do not modify requests and responses beyond what is necessary for authentication and identification. They are often used for content filtering in organizational settings.
Benefits of Using Proxies
Utilizing a proxy server can offer numerous advantages, especially for individuals and businesses concerned about privacy and security.
- Enhanced Privacy: Proxies mask users' IP addresses, making it difficult for websites to track their online activities.
- Access to Restricted Content: Proxies can help bypass censorship and geo-blocks, allowing users to access content that may be unavailable in their region.
- Improved Security: Many proxies offer additional security features such as data encryption and malware filtering, reducing the risk of cyber threats.
- Faster Internet Browsing: Proxies can cache frequently accessed content, leading to quicker load times for users.
Drawbacks of Proxies
While proxies provide many benefits, it's essential to be aware of their limitations and potential drawbacks.
- Limited Security: Not all proxies encrypt data, which may expose users to risks, especially when handling sensitive information.
- Variable Performance: The speed and reliability of proxies can vary significantly, depending on the service provider and server location.
- Legal and Compliance Risks: Using a proxy to bypass geo-restrictions may violate terms of service or legal regulations in some regions.
How to Choose a Proxy
Selecting the right proxy server involves considering various factors that align with your specific needs. Here are some essential criteria to help you make an informed decision:
- Type of Proxy: Determine whether you need an HTTP, HTTPS, or SOCKS proxy based on your requirements.
- Security Features: Look for proxies that offer encryption, data protection, and additional security measures.
- Speed and Reliability: Research the performance of different proxy providers to ensure they can handle your traffic needs efficiently.
- Customer Support: Choose a provider with responsive customer support to assist with any technical issues.
Proxy vs. VPN: What’s the Difference?
While both proxies and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) serve similar purposes in enhancing online privacy, there are key differences between the two technologies:
- Encryption: VPNs encrypt all internet traffic, while proxies may not provide encryption unless specifically designed to do so.
- Traffic Management: VPNs route all traffic through a secure tunnel, whereas proxies typically handle specific applications or protocols.
- Use Cases: VPNs are often favored for secure browsing and data protection, while proxies are popular for bypassing content restrictions.
Proxy Usage in Business
Businesses can significantly benefit from implementing proxy servers to enhance their online security and improve operational efficiency. Key use cases include:
- Content Filtering: Organizations can use proxies to block access to inappropriate or distracting websites, ensuring employees remain focused.
- Data Scraping: Proxies enable businesses to gather data from various sources without being blocked or restricted.
- Improved Network Performance: By caching data, proxies can enhance the speed of internet access for employees.
The Future of Proxies
As online security concerns continue to grow, the role of proxy servers is likely to evolve. Innovations in proxy technology, enhanced encryption methods, and integration with advanced security tools will shape the future landscape of internet privacy.
Furthermore, the increasing use of mobile devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) presents new challenges and opportunities for proxy services. Businesses and individuals alike must stay informed about emerging trends to effectively leverage proxies for enhanced security and privacy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding proxy technology is vital for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of the internet while protecting their online privacy. Proxies offer a range of benefits, from enhanced security to access to restricted content. However, it is equally important to be aware of their potential drawbacks and ensure that the chosen solution aligns with your specific needs.
If you found this article informative, feel free to leave a comment, share it with others, or explore more articles on our website to enhance your knowledge about online privacy and security.
Closing Thoughts
Thank you for taking the time to read our comprehensive guide on proxies. We hope this information proves valuable in your quest for online privacy and security. Don't hesitate to return for more insights and updates on the latest trends in digital safety!
- Wes Brown The Versatile Actor Who Captivates Audiences
- The Simpsons Episode Piddy A Deep Dive Into The Iconic Animation

EP26 Proxy vs reverse proxy by Alex Xu
Guide To Proxy Servers How They Work And Why You Need Them

What Is a Proxy Server Used For? (And How Does It Work?) Kinsta®